The high cost and long time behind bringing a new drug to market: An inside look at pharmaceutical R&D in numbers.
The pharmaceutical industry is the industrial sector that injects the most money into the research and development (R&D) area, in 2022 alone 238 billion dollars were spent.
The cost and time required for pharmaceutical research and development (R&D) can vary widely depending on the type of drug being developed and the stage of development it is in.
According to a 2018 study made by the "Tufts Center for the Study of Drug Development," the average cost to develop a new drug and bring it to market is approximately $2.6 billion. The study also found that the average time from initial discovery to FDA approval is around 10 to 15 years.
However, these figures should be taken as rough estimates. Costs and timing can vary greatly depending on the type of drug being developed and the companies and organizations involved.
Pharmaceuticals focuses on different types of drugs, such as:
- Vaccine development.
- Drug development for orphan diseases.
- Oncology therapies.
- Infectious diseases.
- Orphan diseases: Son aquellas enfermedades, potencialmente mortales y que afectan a una muy pequeña cantidad de personas en el mundo. Este tipo de enfermedades son complejas, como por ejemplo: Enfermedades genéticas, tipos de cáncer poco frecuentes o enfermedades infecciosas. En la UE, una enfermedad es llamada rara cuando afecta a menos de 5 personas por cada 10 000 personas2.
Here you can see different figures showing pharmaceutical development worldwide.
1. New therapies for patients: a look at the number of new active substances approved.
First, pharmaceutical R&D is a complex, time-consuming process involving a wide range of activities, including basic research, preclinical development, clinical trials and regulatory approval. The process begins with basic research to identify potential molecules and develop new compounds. This may involve detecting a large number of compounds to identify those with the desired properties, and then conducting laboratory studies to determine their safety and efficacy.
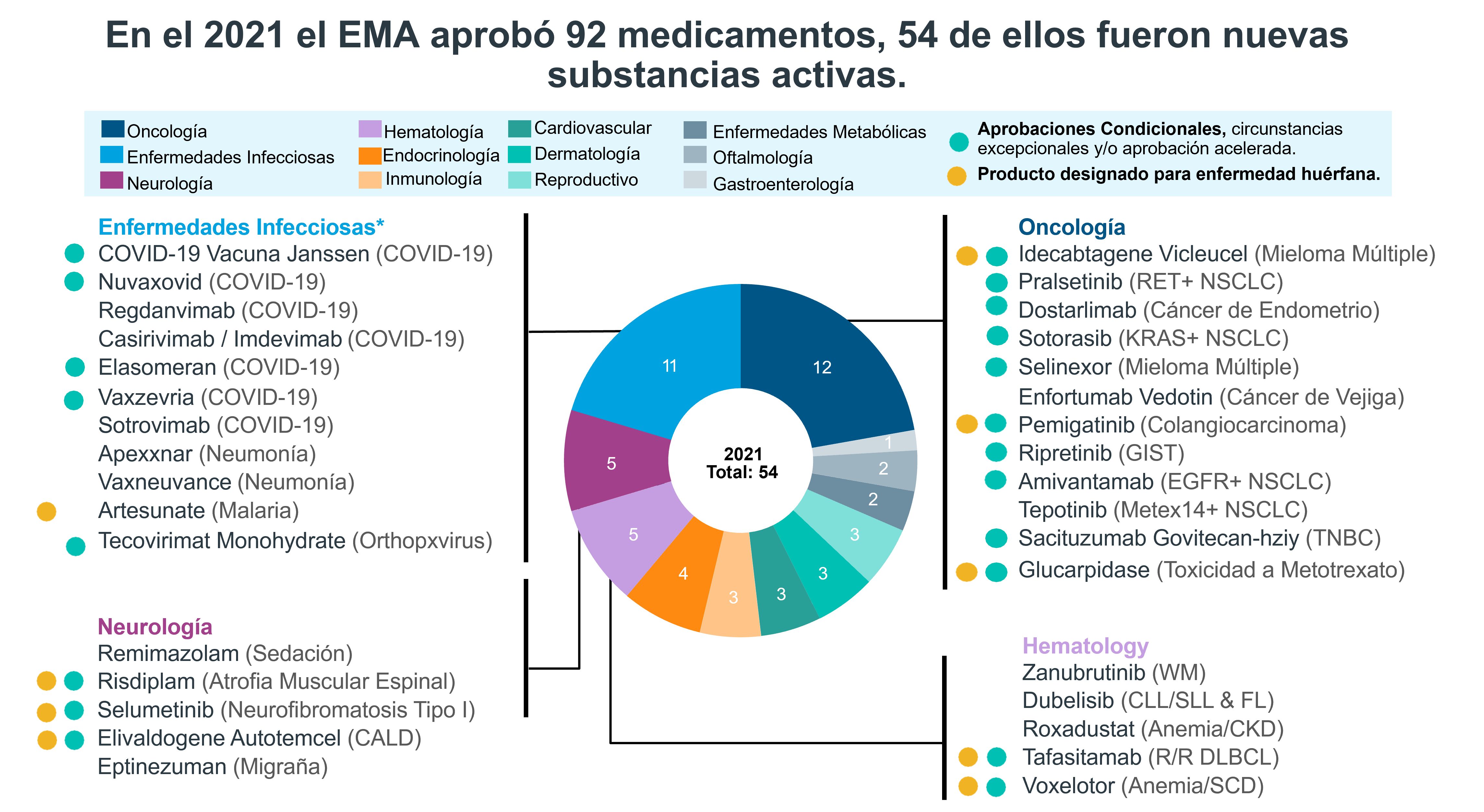
For a new drug to be marketed, it must be approved by a regulatory organization. An indicator of pharmaceutical progress is thus the number of active substances approved per year.
- Active Substance or Active Ingredient: It is the molecule in a drug responsible for generating a direct effect on the cure, treatment or prevention of a disease.
Some regulatory entities are:
- FDA: Food and Drug Administration (USA) – (https://www.fda.gov).
- EMA: European Medicines Agency (Unión Europea) – (https://www.ema.europa.eu/en).
- ANVISA: Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária (Brasil) – (https://www.gov.br/anvisa/pt-br).
- INVIMA: Instituto Nacional de Vigilancia de Medicamentos y Alimentos (Colombia) – (https://www.invima.gov.co)
The year 2021 was the year of new drugs for infectious diseases due to the SARS-CoV-2 virus. In 2021 the EMA (European Medicines Agency) increased its approval of medicines by 28% compared to 2020.
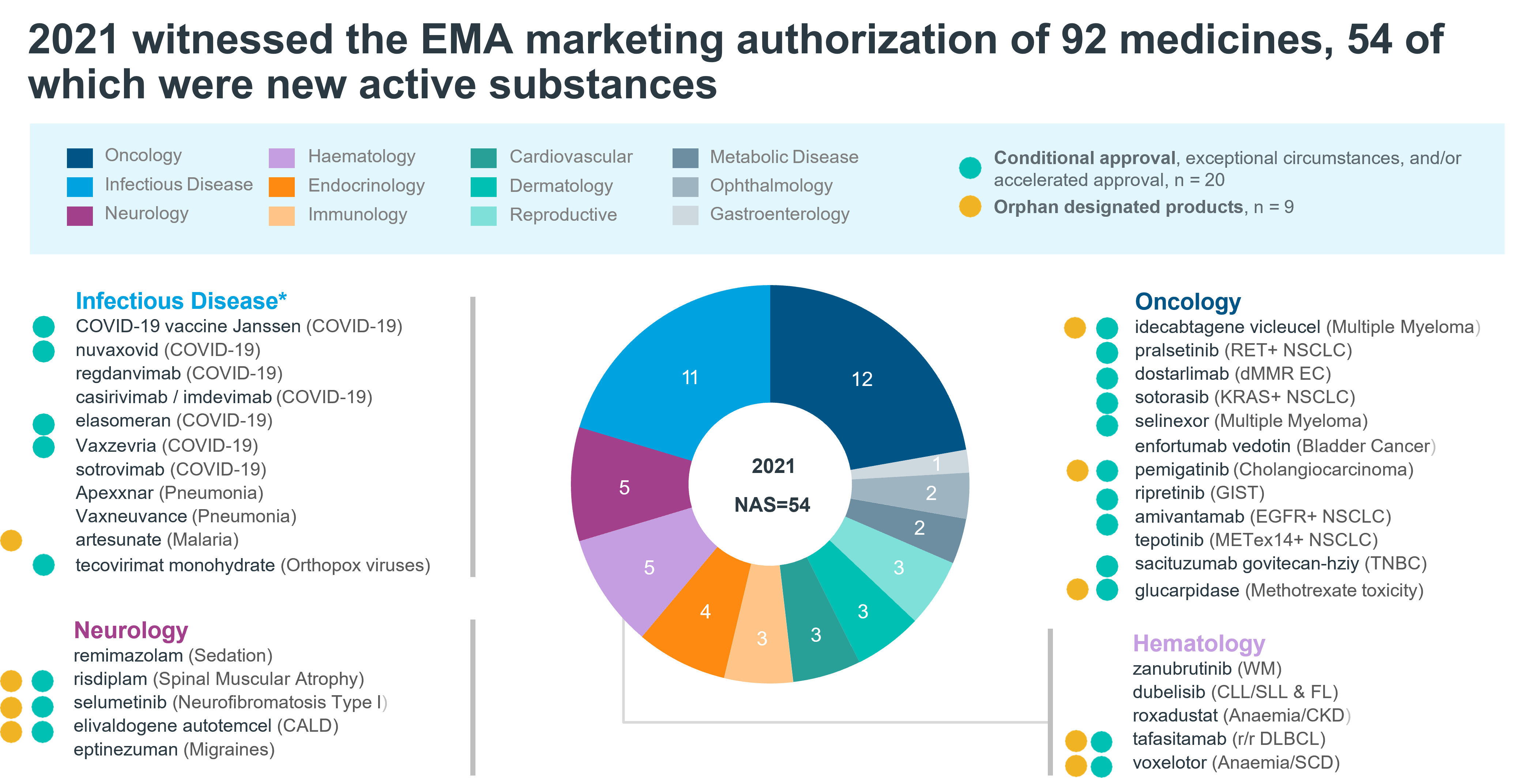
Image taken from: IQVIA | EFPIA Pipeline Innovation Review 2022
2. Monitoring the growth of clinical trials: a look at the number of trials performed per year.
Now, once a drug candidate has shown promise in preclinical studies, it moves on to clinical trials.
These tests are carried out in three different phases. Each phase designed to assess different aspects of the safety and efficacy of the medicinal product.
- Phase I trials involve a small number of healthy volunteers, ranging from 15 to 20 patients. They are designed to assess the safety of the drug and possible side effects.
- Phase II trials involve a larger number of patients, approximately 100 patients. They are designed to evaluate the efficacy of the drug.
- Phase III trials are large, randomized, controlled trials that are conducted to confirm the efficacy and safety of the drug, and to generate data that can be used to support regulatory approval. Thousands and even hundreds of thousands of patients from all over the world participate.
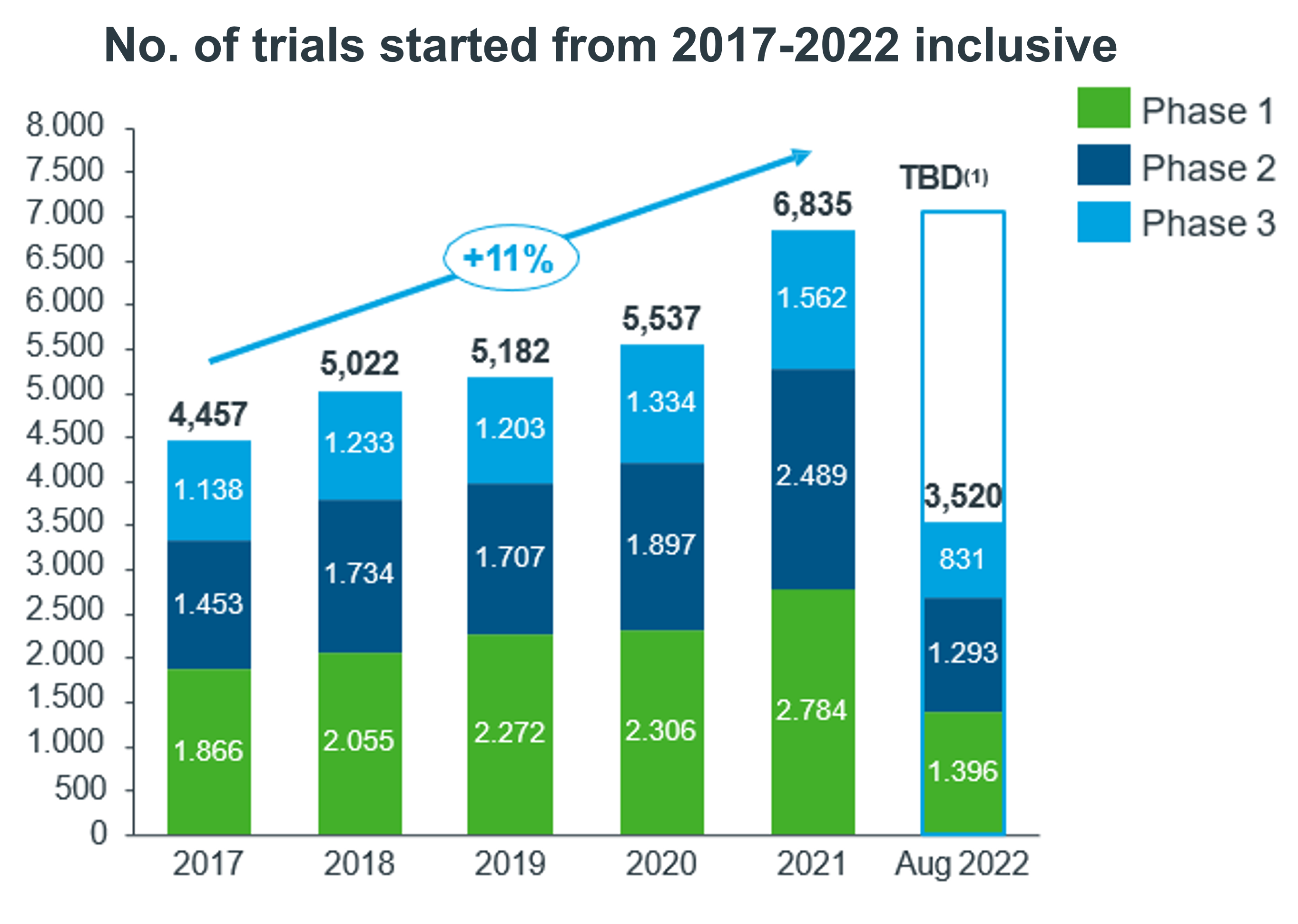
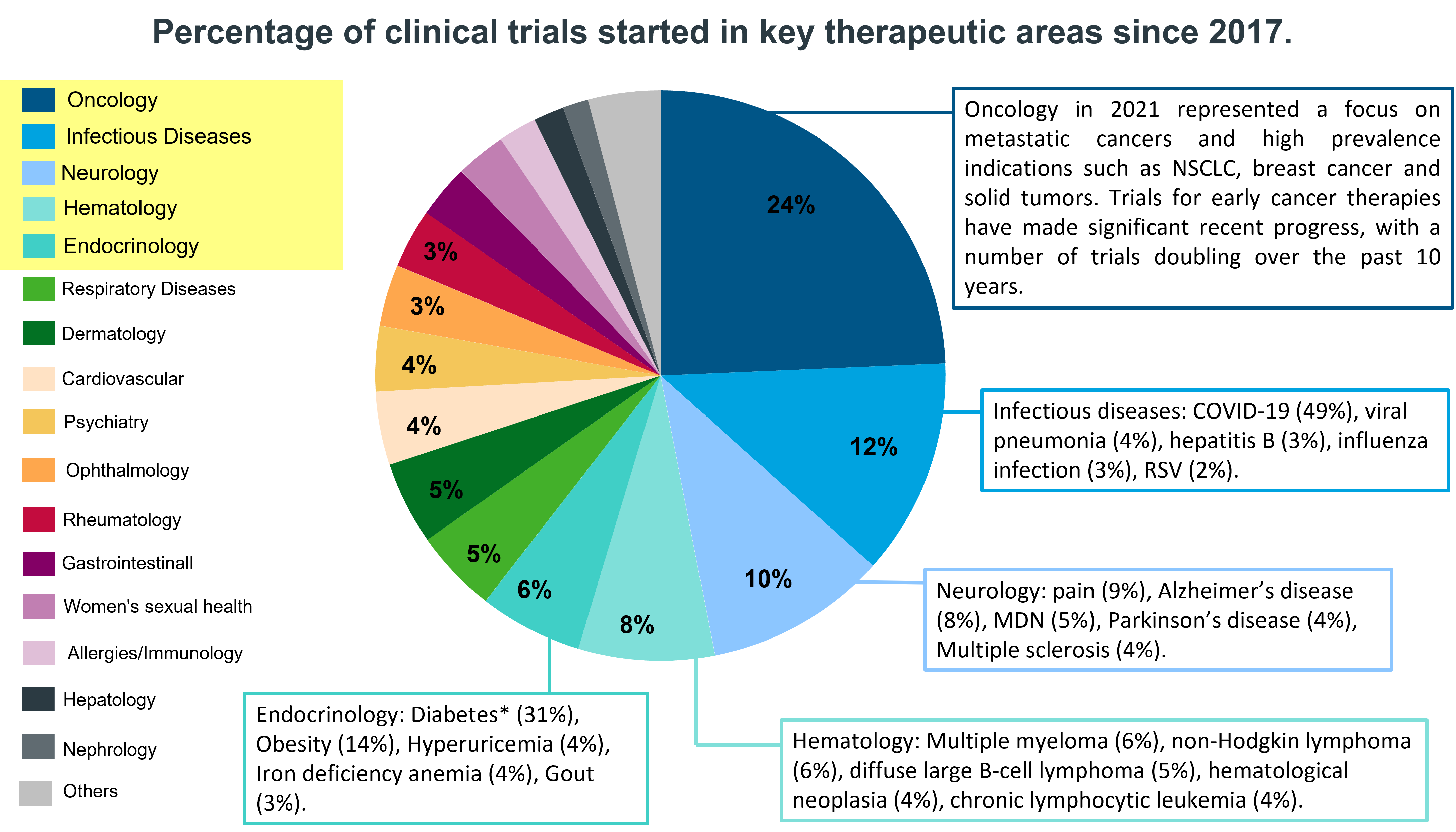
By August 2022, 3 520 phases of clinical trials had begun. The medical areas where more clinical trials were initiated were: Oncology, Infectious Diseases, Neurology, Hematology and Endocrinology.
Upon completion of clinical trials, the proprietor of the medicinal product submits an Application for New Medicinal Products (NDA) or a Licence Application for Biological Products (BLA) to the relevant regulatory agency, such as the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or the European Medicines Agency (EMA), for review and approval.
However, the review process may take several months or even years, and the agency may require additional information or studies before approving the drug.
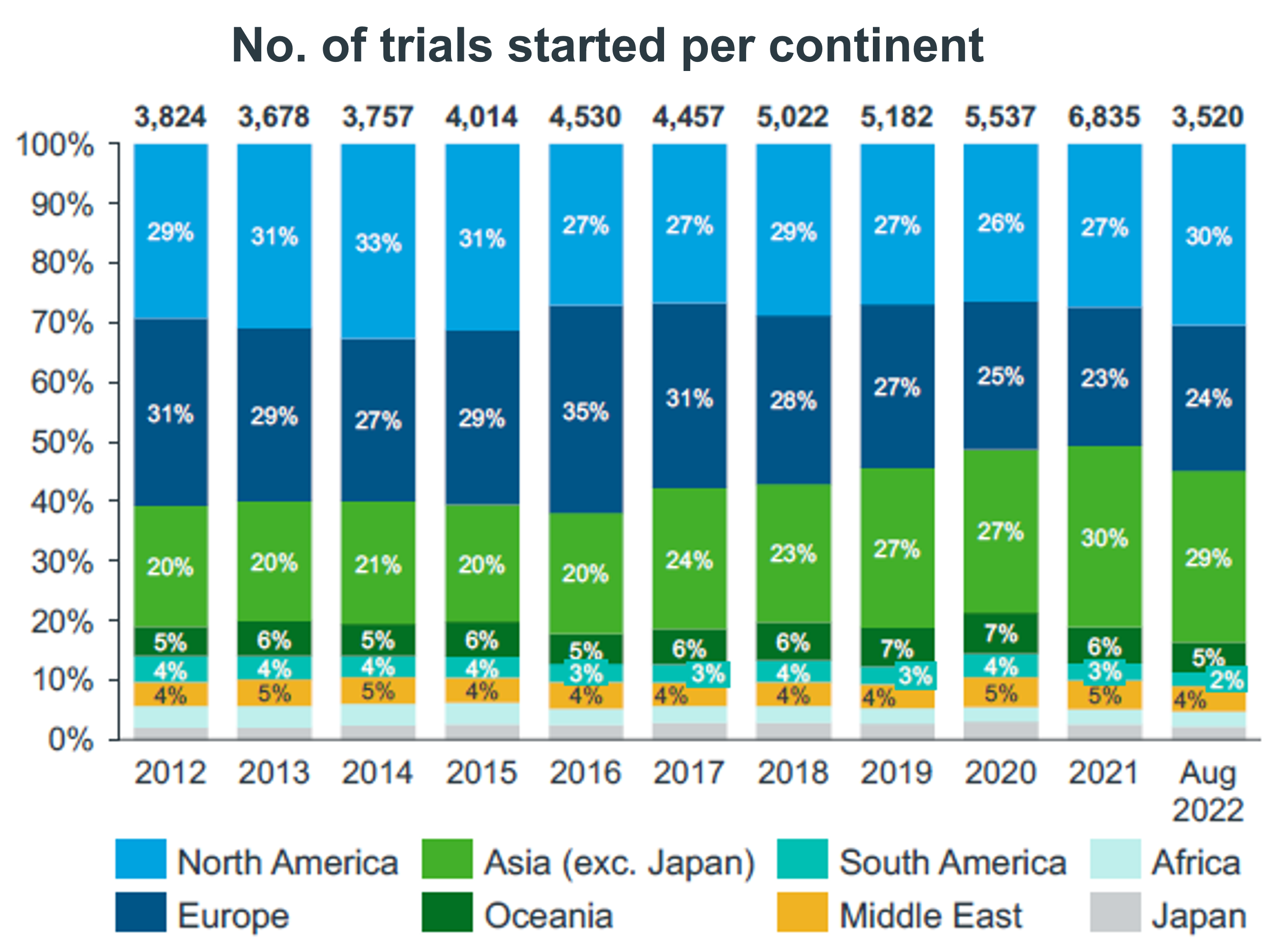
2.1 Exploring the distribution of clinical trials on continents: where clinical research is occurring.
The distribution of clinical trials across continents may vary depending on a number of factors, including the availability of funds, infrastructure, and patient populations.
North America (United States and Canada) and Europe are considered important centers for clinical trials, with a significant number of trials taking place in these regions. According to a 2019 report from the Tufts Center for the Study of Drug Development, more than half of all clinical trials were conducted in these two regions.
In North America, most clinical trials are conducted in the United States, which has a large and diverse population and a well-established regulatory system. According to data from ClinicalTrials.gov, in 2021, the United States had the highest number of registered clinical trials of any country in the world, with more than 200,000 trials.
In Europe, most clinical trials are conducted in Western European countries, such as the UK, Germany and France. According to data from the European Clinical Trials Database, in 2021, these countries had the highest number of registered clinical trials in Europe.
3. A deeper look at key therapeutic areas in pharmaceutical R&D.
Pharmaceutical companies focus their research and development efforts on a wide range of therapy areas. This with the aim of developing new treatments for a variety of diseases. Some of the key therapeutic areas for R&D in the pharmaceutical industry include:
3.1 Examples of key therapeutic areas in pharmaceutical R&D.
- Cancer: It has been a major focus of pharmaceutical R&D for many years. Companies focus on a wide range of cancers, including breast, lung and prostate cancer.
- Cardiovascular diseases: They are one of the leading causes of death worldwide. It is key to prevent and manage these conditions such as heart failure, hypertension and hyperlipidemia.
- Neurology: Neurology is another key therapy area for R&D in the pharmaceutical industry. The neurological disorders of greatest interest are Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis.
- Metabolic diseases: Metabolic diseases such as diabetes and obesity are becoming more common around the world. Pharmaceutical companies are working to develop new treatments to manage these conditions.
- Immunology: With the growing understanding of the immune system, pharmaceutical companies develop therapies for autoimmune diseases, allergies and transplants.
- Infectious diseases: Infectious disease research is another key area for pharmaceutical R&D. Some diseases of interest are HIV, flu and malaria.
- Orphan drugs: Orphan drugs are drugs developed to treat rare diseases. They are often overlooked by pharmaceutical companies because they affect only small patient populations.
These are just a few examples of the many areas of therapy in which pharmaceutical companies focus their R&D efforts, as well as research in personalized medicine and gene therapy. The choice of therapy area is driven by a combination of factors, including unmet medical needs, the science behind the disease and the regulatory environment.
Conclusion.
Finally, the pharmaceutical R&D process is long, complex and costly and requires significant resources from stakeholders.
North America and Europe are important centers for clinical trials, with a significant number of trials in these regions. Asia and Latin America are also becoming increasingly important centers for clinical trials.
In short, pharmaceutical R&D is a complex and costly process that requires significant resources and expertise. It is important to consider the costs, timing and distribution of clinical trials when assessing the status of R&D. The number of new active substances approved is also an important measure for monitoring the success of R&D.
Referencias:
1. Worldwide pharmaceutical R&D spending 2014-2028 | Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/309466/global-r-and-d-expenditure-for-pharmaceuticals/.
2. EUROPEAN COMMISSION - GENERAL BUREAU FOR HEALTH AND CONSUMER PROTECTION.
3. IQVIA/EFPIA Pipeline Review 2021. https://www.efpia.eu/publications/downloads/efpia/iqviaefpia-pipeline-review-2021/.
4. Tufts CSDD. https://csdd.tufts.edu/.
